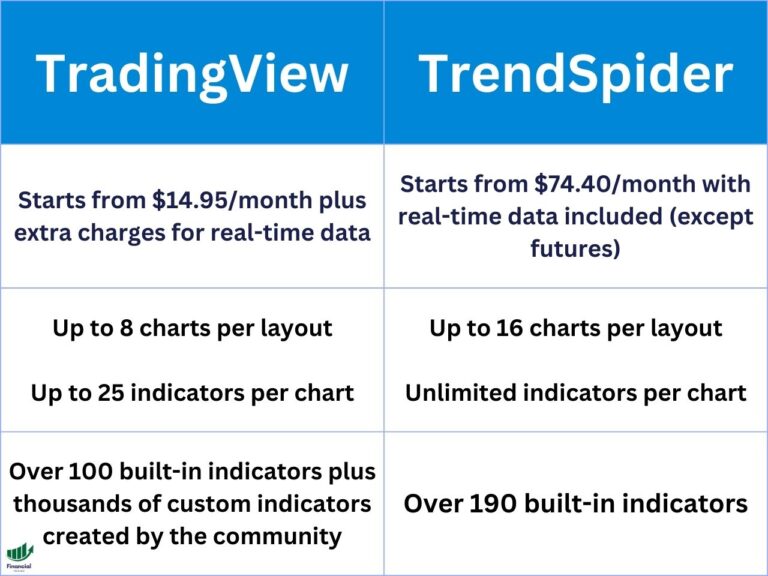
What is a Short Put (Naked Put)? | Uncovered Put Strategy
The short put options trading strategy is an excellent way to generate passive income on the stock market.
A short put strategy has a high probability of profit, meaning you will win most of your trades.
However, even if you win more than 80% of the time, it only takes one bad trade to ruin a string of winners.
What is a Put Option?
A put option is a contract that gives the owner the right but not the obligation to sell 100 shares of a stock at the strike price.
When you buy a put option, you are essentially buying stock insurance to minimize your loss if the stock price falls.
On the other hand, the put seller is collecting a premium while promising to buy 100 shares at the strike price.
What is a Short Put (Uncovered Put)?
A short put is also known as a naked or an uncovered put and is when you sell to open a put option to collect a premium from the buyer.
The short put is a bullish to neutral position, meaning you want to underlying stock to move up or go sideways to make a profit on the trade.
When trading a short put strategy, you risk much more than your profit potential.
Therefore, if you don’t plan on taking assignment of the shares, you should use a stop loss to limit your risk.
Additionally, you can add a call credit spread to the short put, creating a jade lizard options strategy.
Short Put vs. Cash-Secured Put
The only difference between a short put and a cash-secured put is that a short put requires just 20% of the capital as a cash-secured put.
For example, if you sell a cash-secured put with a $100 strike price, you must set aside $10,000 for your broker.
The short put will only require you to set aside about $2,000, providing you with around 5x leverage.
The cash-secured put and short put are the same trade. The only difference is the amount of money you must set aside to open the trade.
Selling puts with leverage is a high-risk strategy that only experienced traders who understand the risks should use.
Long Put vs. Short Put
A long put is the exact opposite of a short put. Instead of selling a put to open, you buy a put to open.
Put buyers pay a premium, while the put sellers collect the premium.
Traders and investors may use long puts to hedge their portfolios if the stock market falls.
Additionally, you can purchase a lower strike long put to make a short put a defined risk vertical credit spread.
Risks of Short Puts
In the worst-case scenario, you can get assigned 100 shares of stock for each uncovered put contract you sell.
Short put strategies may also incur a loss if the implied volatility increases. When you sell options, you are betting that the stock will increase and volatility will decrease.
If you want to reduce some of the risk involved with a short put, you can buy a long put with a lower strike price, turning the short put into a defined risk put credit spread.
Short Put Example
On 10/18/2022, AAPL stock closed at around $144 per share.
As you can see from the chart below, the recent low is about $130 per share. Additionally, the implied volatility is relatively high, which means options are more expensive than usual.
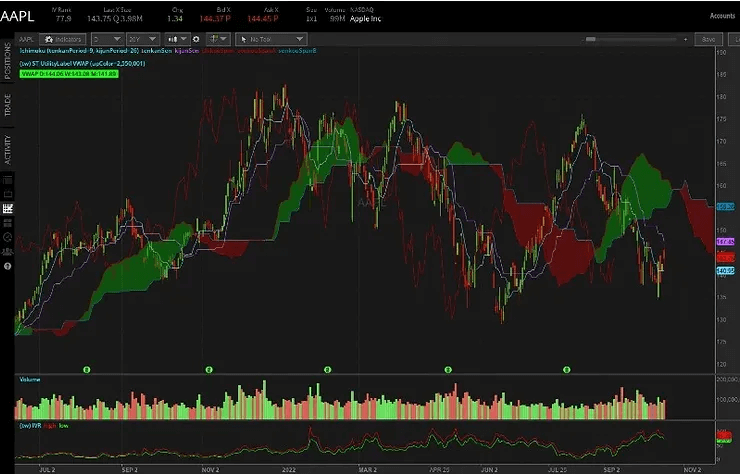
To take advantage of the high volatility in the market, instead of buying shares of AAPL stock, you can sell a put at the $120 strike price around 90DTE and collect a $300 premium.
If AAPL stock stays above the $120 strike price at expiration, the short put will expire worthless, and you keep all the premium.
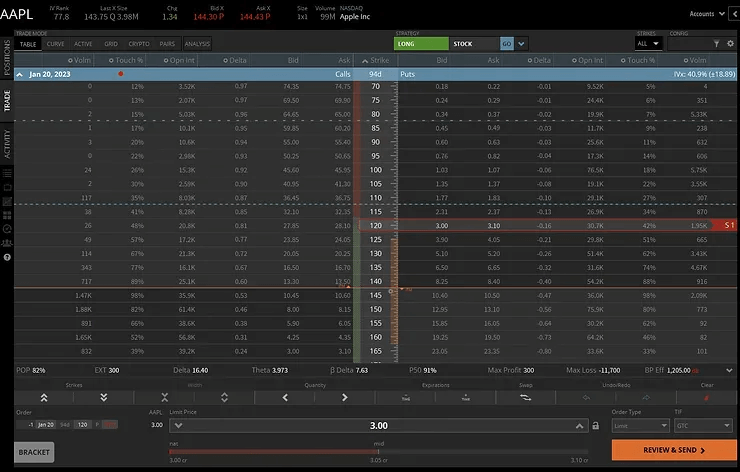
However, most traders will take profit early on a trade like this when you collect around 50-60% of the premium.
If AAPL stock falls below $120 per share, you will potentially be obligated to buy 100 shares of AAPL at $120.
However, if you use a stop loss before it goes ITM, this cannot happen since you can only get assigned on puts that are ITM.
Short Put Strategies: Bottom Line
The short put is a high-probability strategy that allows you to make money in flat or bullish markets.
If you are new to options trading, the short put is best replaced with the cash-secured put so you aren’t able to use too much leverage and blow up your account.
The only difference between a short put and a cash-secured put is whether you can accept assignment of the shares or not.
If you know how to use stop losses and manage your risk, the short put strategy is fine, but new traders should learn by trading cash-secured puts instead.
Additionally, you can sell short puts on futures options to improve their tax treatment.
Before you go
If you want to keep educating yourself about personal finance, you must check out these posts as well:
What is the Most Successful Options Strategy
Options Trading for Income: The Complete Guide
Mark Minervini’s Trading Strategy: 8 Key Takeaways
The Best Options Trading Books
Get Your Free Trading Resources
Grab the free trading journal template plus the same tools we use to stay organized, consistent, and objective.
- Free trading journal template
- Custom indicators, watchlists, and scanners
- Access our free trading community
Enter your email below to get instant access.
No spam. Unsubscribe anytime.