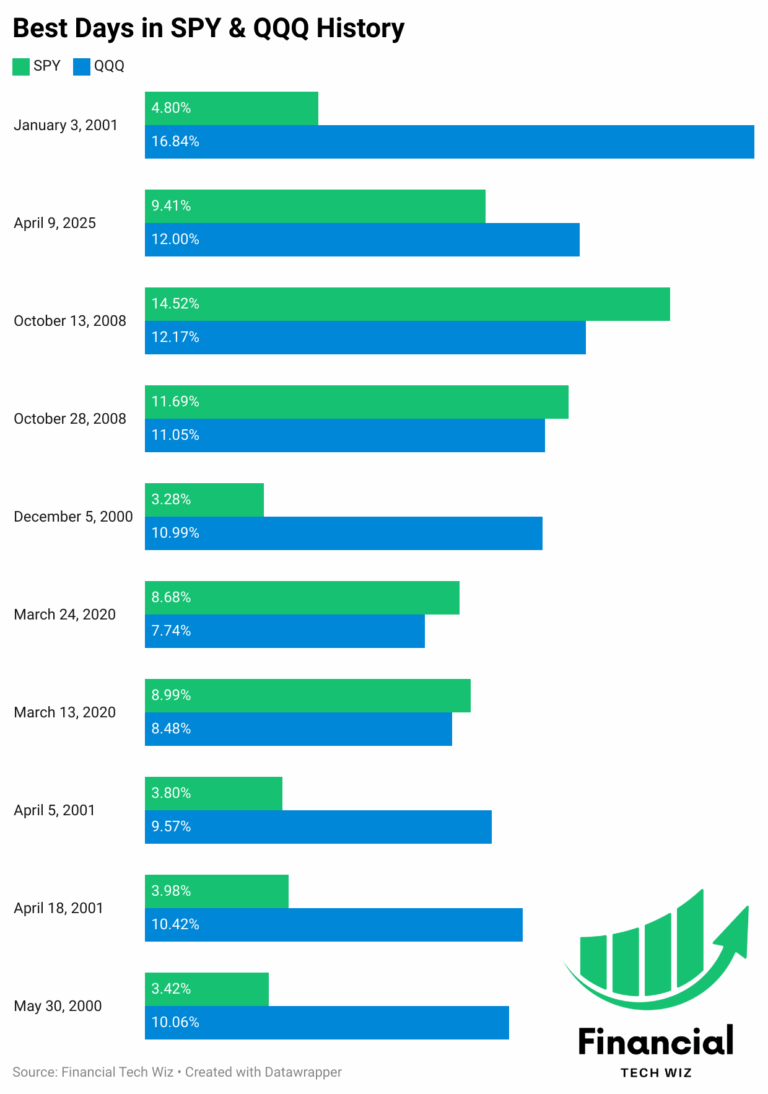
Top 10 Best Days in Stock Market History For SPY & QQQ
The stock market has seen some incredible one-day rallies, where both the S&P 500 (SPY) and Nasdaq 100 (QQQ) indices experienced massive percentage gains in a single trading session. These explosive gains are often fueled by major market events, such as central bank interventions, government stimulus measures, or economic recovery signals after a period of…